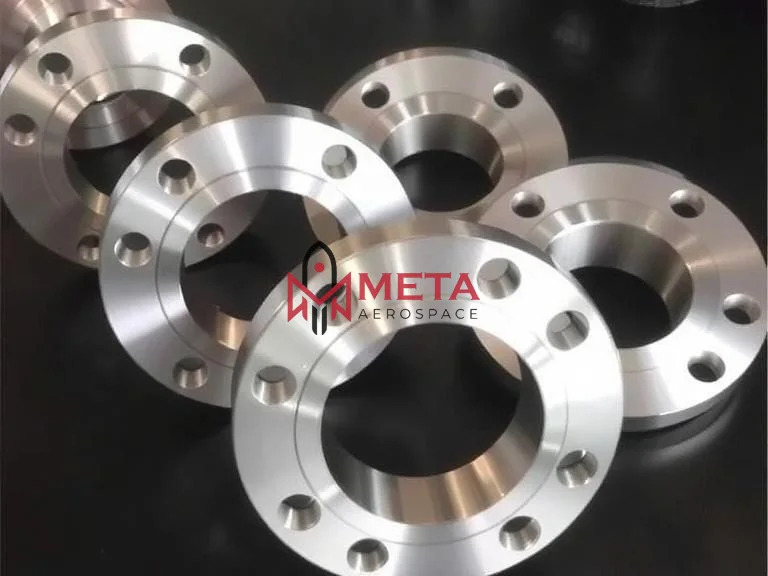
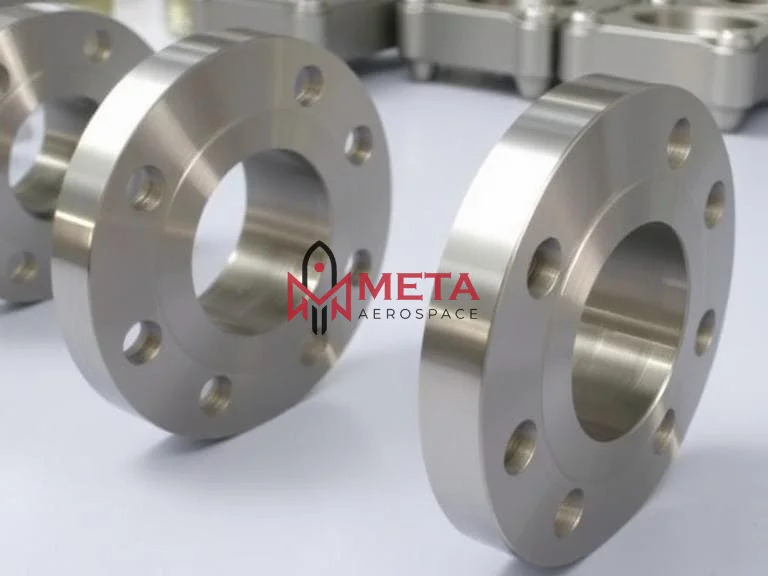
Inconel 625 Flanges
Inconel 625 Flanges Specification
- Feature
- Corrosion Resistant, High Strength, Oxidation Resistance, Durability
- Application
- Petrochemical Industry, Power Plants, Offshore, Chemical Processing, Aerospace, Marine Engineering
- Purity
- Nickel content approximately 58% minimum
- Grade
- UNS N06625, Alloy 625
- Dimension (L*W*H)
- As per drawing or ASTM/ASME standard
- Product Type
- Pipe Flange
- Material
- Inconel 625 (Nickel-Chromium Alloy)
- Standard
- ASTM B564, ASME SB564, DIN, EN, JIS, GB, IS, BS
- Shape
- Round, Square, Custom
- Surface
- Bright, Black, Polished, Rough
- Connection
- Weld Neck, Slip On, Threaded, Blind, Socket Weld, Lap Joint
- Technics
- Forged, Machined
- Pressure
- Class 150 to 2500 LBS, PN6 to PN400
- Size
- 1/2 inch to 48 inch (DN15 to DN1200)
- Color
- Silver, Metallic Grey
- Face Type
- RF (Raised Face), FF (Flat Face), RTJ (Ring Type Joint)
- Hardness
- Rockwell B100 Max
- Density
- 8.44 g/cm
- End Finish
- Smooth, Serrated, Spiral Serrated
- Elongation
- 30% Min (in 2 inches)
- Packaging
- Wooden Cases/Pallets, Plastic Wrap, Custom Packaging
- Yield Strength (0.2% Offset)
- 414 MPa min (60 ksi)
- Melting Point
- 12901350C
- Tensile Strength
- 827 MPa min (120 ksi)
About Inconel 625 Flanges
What Are Specification Inconel 625 Flanges?
| Standards | GOST Flange, JISB2220, BS1560-3.1, API7S-15, API7S-43, API605, EN1092, BS, BS4504, BS 10, EN-1092, DIN, ANSI, ASME, DIN, MSS S44, ISO70051, ANSI/ASME B16.5, ASME/ANSI B16.5/16.36/16.47A/16.47B, B16.47 Series A & B, B16.48, EN |
|---|---|
| Pressure Rating ANSI | Class 1500, Class 150, Class 900, Class 2500, Class 300, Class 600, |
| Pressure Calculation in DIN | 10Bar, 16Bar, 25Bar, 40Bar, 6Bar, / PN16, PN64, PN40, PN25, PN10, PN6 |
| JIS | 16 K, 20 K, 5K, 10 K, 40 K, 63 K, 30 K, |
| UNI | 10Bar 16Bar 6Bar 25Bar 40Bar |
| EN | 6Bar 25Bar 40Bar 10Bar 16Bar |
| Most common Types | Threaded / Screwed / Forged / Plate |
| Production technique | Forged, Heat treated and machined |
| Shapes and Types we produce | Large Male-Female (LMF), Ring Type Joint (RTJ), Flat Face (FF), Small Tongue, Small Male-Female (SMF),Raised Face (RF), Large Tongue & Groove, Groove, Lap-Joint Face (LJF) |
| Test | Direct-reading Spectrograph, Magnetic particle detector, Hydrostatic testing machine, X-ray detector, UI trasonic flaw detector |
| Equipment | Pushing Machine, Press machine, Bending machine, Sand-blasting machine, electric bevelling machine etc |
Equivalent material Of Inconel 625 Flanges?
| Element | Density | Melting Point | Tensile Strength | Yield Strength (0.2%Offset) | Elongation |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Inconel 625 | 8.4 g/cm3 | 1350 ?C (2460 ?F) | Psi ? 1,35,000 , MPa ? 930 | Psi ? 75,000 , MPa ? 517 | 42.5 % |
Chemical Composition Of Inconel 625 Flanges?
| Element | Density | Melting Point | Tensile Strength | Yield Strength (0.2%Offset) | Elongation |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Inconel 625 | 8.4 g/cm3 | 1350 ?C (2460 ?F) | Psi ? 1,35,000 , MPa ? 930 | Psi ? 75,000 , MPa ? 517 | 42.5 % |
Mechanical Properties Of Inconel 625 Flanges?
| Grade | C | Mn | Si | S | Cu | Fe | Ni | Cr |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Inconel 625 | 0.10 max | 0.50 max | 0.50 max | 0.015 max | ? | 5.0 max | 58.0 min | 20.0 ? 23.0 |
Superior Corrosion and Oxidation Resistance
Inconel 625 flanges are engineered to withstand highly corrosive and oxidizing environments, ensuring long-term structural integrity. The nickel-chromium composition, with at least 58% nickel, renders these flanges highly resistant to pitting, crevice corrosion, and stress-corrosion cracking. This makes them ideal for offshore, marine, chemical, and power plant applications where durability is paramount.
Exceptional Mechanical Strength and Versatility
With a minimum tensile strength of 827 MPa and yield strength of 414 MPa, Inconel 625 flanges maintain high performance even at elevated temperatures up to their melting range of 12901350C. Their adaptability across a range of sizes (1/2 inch to 48 inches), connection types, and pressure classes (Class 150 to 2500 LBS, PN6 to PN400) makes them suitable for diverse industries and custom applications.
Comprehensive Standards and Quality Assurance
Manufactured to rigorous industry standards including ASTM B564, ASME SB564, DIN, EN, JIS, GB, IS, and BS, Inconel 625 flanges undergo strict quality controls. Available in various finishes and packaging options, these flanges can be tailored to specific client requirements, guaranteeing performance, safety, and reliability throughout their lifespan.
FAQs of Inconel 625 Flanges:
Q: How are Inconel 625 flanges typically used in industrial applications?
A: Inconel 625 flanges are commonly employed in petrochemical plants, power stations, marine engineering, aerospace, and chemical processing industries. Their excellent resistance to corrosion and high mechanical strength make them ideal for connecting piping systems or equipment exposed to aggressive chemicals or severe operating conditions.Q: What are the benefits of selecting Inconel 625 flanges over traditional stainless steel flanges?
A: Choosing Inconel 625 flanges offers superior resistance to high-temperature oxidation, chloride-induced stress-corrosion cracking, and aggressive chemical environments. They provide enhanced durability and longevity, reducing maintenance needs and ensuring performance in challenging applications where standard stainless steel may fail.Q: When should I opt for a specific flange face type like RF, FF, or RTJ?
A: Flange face type selection depends on the sealing requirements, pressure ratings, and application environment. Raised Face (RF) is widely used for general process piping, Flat Face (FF) suits low-pressure or cast iron systems, while Ring Type Joint (RTJ) is ideal for high-pressure, high-temperature scenarios, enhancing gasket compression and sealing integrity.Q: What manufacturing process is used for Inconel 625 flanges?
A: These flanges are typically produced through forging and machining, yielding superior grain structure and mechanical properties. This process ensures material uniformity, dimensional accuracy, and the ability to withstand demanding service environments.Q: Where are Inconel 625 flanges exported or supplied from?
A: As exporters, manufacturers, suppliers, and traders based in India, these flanges are shipped globally to meet international demands, adhering to relevant ASTM, ASME, and other standards. Custom packaging options such as wooden cases, pallets, and plastic wrap ensure safe transit.Q: How does the end finishsuch as smooth, serrated, or spiral serratedimpact flange usage?
A: End finish determines the sealing effectiveness between the flange and gasket. Smooth finishes suit soft gaskets and moderate pressure, serrated surfaces enhance gasket grip for higher pressure applications, while spiral serrated finishes improve seal integrity under cyclic thermal and mechanical conditions, making them suitable for critical services.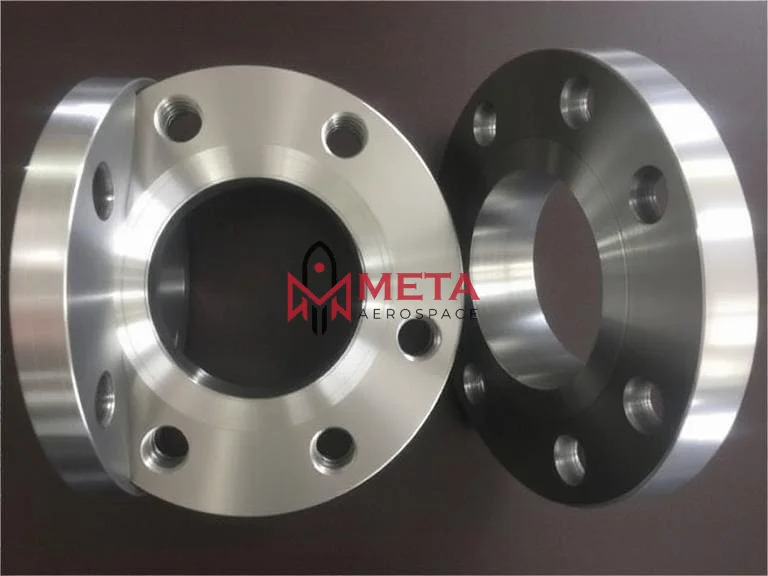

Price:
- 50
- 100
- 200
- 250
- 500
- 1000+
More Products in Inconel Flanges Category
Inconel 601 Flanges
Material : Inconel 601
Standard : Other, ASTM, ASME, DIN, EN, JIS, BS, UNI, GOST
Size : 1/2 to 48 (DN15 to DN1200)
Grade : Inconel 601 (UNS N06601)
Surface : Other, Bright, Polished, Black, CNC Machined
Technics : Other, Forged / Cast
Inconel 600 Flanges
Material : Inconel 600 (NickelChromium Alloy)
Standard : Other, ASTM B564, ASME SB564, DIN, EN, JIS, BS, GB, GOST
Size : 1/2 to 48 (DN15~DN1200)
Grade : Inconel 600 / UNS N06600
Surface : Other, Polished / Mill Finish
Technics : Other, Forged
Inconel 718 Flanges
Material : Inconel 718
Standard : Other, ASTM B564, ASME SB564
Size : 1/2 to 48
Grade : Inconel 718 (UNS N07718)
Surface : Other, Smooth, Nickel Plated
Technics : Other, Forged
Inconel Round Flanges
Material : Stainless Steel
Standard : ANSI
Size : Various Sizes Available
Grade : Multple Grades Available
Surface : Galvanized
Technics : Hot Rolled
 Send Inquiry
Send Inquiry Send Inquiry
Send Inquiry




 English
English Spanish
Spanish French
French German
German Italian
Italian Chinese (Simplified)
Chinese (Simplified) Japanese
Japanese Korean
Korean Arabic
Arabic Portuguese
Portuguese